What Are You Looking For?
Basic Concepts of Lithium Ion Batteries
May 22, 2025Basic Concepts of Lithium Ion Batteries
1. Lithium-ion battery fundamentals:
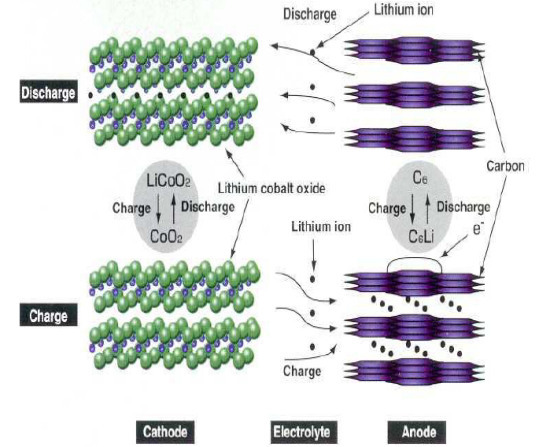
Take the lithium cobalt oxide-graphite system as an example:
1.1 The reaction that occurs on the positive electrode is:
LiCoO2 = Li1-xCoO2 xLi xe- (electron)
1.2 The reaction that occurs on the negative electrode is:
6C xLi xe- (electron) = LixC6
2. Basic Concepts:
Voltage: The voltage of the electrical appliance is 3.0-4.2/2.5-4.2 (unit: V), when discharging, the voltage keeps dropping, the platform voltage refers to the voltage that accounts for the vast majority of the entire discharge time, the general nominal voltage is the central voltage of the platform voltage, near this voltage, the voltage changes very slowly when charging and discharging.
Internal resistance: refers to the total resistance of the battery to the flow of current, the electrochemical impedance of the cell itself, including the ohmic resistance nuclear chemical resistance, and the influence of the internal resistance on the discharge characteristics is particularly obvious (unit: mΩ) when the high current is discharged. The higher the internal resistance, the more heat is generated when the battery is discharged, the energy loss increases, and the effective output capacity decreases.
Capacity: refers to the amount of electricity that can be obtained from the battery under certain discharge conditions, that is, the integration of current to time (unit: mAh or Ah). Capacity (Q) = Current (I) × Discharge Time (t)
ACEY-BCT506-512H 18650 cell capacity tester is an important equipment for lithium battery production and testing, its main role is to carry out capacity testing and performance screening of lithium batteries to ensure the quality level and consistency of the battery.If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us at any time.
Rate: refers to the expression of the discharge capacity of the cell when it is discharged according to the multiple of the nominal capacity.
Cycle: refers to the number of cycles when the secondary battery is charged and discharged according to a certain system, and its performance is attenuated to a certain extent.
Storage Performance: Storage performance. After the battery is stored for a period of time, the performance will change due to the influence of some factors, resulting in battery self-discharge, electrolyte leakage, battery short circuit, etc.
Discharge characteristics: refers to the stability of the battery's working voltage, the level of the voltage platform and the high-current discharge performance under a certain discharge system, which indicates the ability of the battery to replace the load.
IEC61960 specifies that the rules for common cylindrical batteries are as follows:
Cylindrical battery, 3 letters followed by 5 numbers. 3 letters, I for built-in lithium ion and L for lithium metal or lithium alloy electrode. The second letter represents the cathode material, C for cobalt, N for nickel, M for manganese, and V for vanadium. The third letter is R for cylindrical shape.
5 digits, the first 2 digits indicate the diameter and the last 3 digits indicate the height, all in mm.For example, ICR 18650 is a universal 18650 cylindrical battery with a diameter of 18mm and a height of 65mm.
3. The basic structure of lithium-ion batteries
3.1 Positive electrode construction
Active Substances, Conductive Agents, Binders, Current Collectors (Aluminum Foil)
K-tech Cathode Formulation:
|
Component |
Material |
Proportion |
|
Active Material |
Ternary Li(Co1-x-yNixMnyO2) |
93.5%-96.5% |
|
Conductive Agent |
Conductive carbon black (SP), Conductive graphite (KS-6) |
1.5%-4% |
|
Binder |
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) |
2.0%-2.5% |
|
Current Collector |
Aluminum foil |
- |
3.2 Negative electrode construction
Active Substances: Conductive Agents, Thickeners, Binders, Current Collectors (Copper Foils)
L-tech Anode Formulation:
|
Component |
Material |
Proportion |
|
Active Material |
Artificial Graphite (C) |
93.5%-95.6% |
|
Conductive Agent |
Conductive carbon black (SP), Conductive graphite (KS-6) |
1.0%-2.5% |
|
Thickener |
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) |
1.3%-1.5% |
|
Binder |
Styrene-butadiene rubber latex (SBR) |
2.1%-2.5% |
|
Current Collector |
Copper foil |
- |
3.3 Diaphragm construction
Structure and characteristics of polyolefin separator
|
Structure |
Material |
Production Method |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Application Scope |
|
Single-layer, Double-layer |
PP |
Dry process |
Good thermal resistance, good permeability |
Safety shutdown temperature (closure temperature > 140°C) is higher than PE |
Digital batteries, Power batteries |
|
Single-layer, Double-layer |
PE |
Dry process, Wet process |
High mechanical strength, low-temperature closure (around 130°C) |
Poor high-temperature resistance compared to PP |
Digital batteries |
|
Triple-layer |
PP/PE/PP |
Dry process |
Combines the advantages of PP and PE films, good mechanical strength, higher safety |
Poor high-temperature permeability |
Digital batteries |